The following procedures must be carried out every time an LVS is installed in a new location.
These procedures must be performed to correctly install and align the scan head and define the scan area for vehicles to drive through during scanning.
The exact procedure for physical installation, and the mechanism for scan head alignment adjustments will depend on the scan head mounting design.
The following instructions are not specific to a particular mounting system but all specified dimensions relate to standard installation for on-road truck and trailer units.
For larger off-highway dump trucks, higher mounting and/or wider scan track may be required.
Contact your Loadscan representative for assistance with application-specific installation requirements.
Step 1 – Select a suitable site
- The scan area must be level, or of even gradient not exceeding 5 degrees (9%) and maximum 3-degree (5%) camber.
- The scan area must allow for a 3m (10’) track width, for at least a full truck length before and after the scan head, with a minimum of 6m (20’) of physically restricted width each side.
- Truck and trailer units must:
- have suitable unobstructed access
- be able to approach, pass under and drive clear of the scanner (back of trailer clear of scan head) maintaining a straight line of travel, in either direction throughout.
- A concrete pad is ideal but any hard, non-dusty surface with suitable markers/barriers is adequate.
- The site must be in a dust-controlled environment where only low levels of dust or other visual pollutants in the air are expected.
- 110-240 VAC mains (line) power is required, (except for 24 VDC option).
A suitable power conditioner/surge suppressor should be used to protect the LVS equipment where power quality is poor.
All LVS components should be powered from the same branch circuit.
(Note for Europe: 16A maximum branch circuit breaker, maximum 3m power cord between outlet and power box).A generator with a capacity of at least 1.0 kVA may be used.
Loadscan suggests only inverter-type generators are used and recommends the Honda EU 20i, as it produces good quality power.
- Weather-proof housing is required for the operator console, printer and power box. A site office, portable container/building or sealed kiosk is suitable.
- The operator console can be bench or wall mounted and connects to the power box with a 1.5m (5’) flexible cable. Labelled cable connection ports can be found at the rear of the console.
- The scan head connects to the power box with a flexible cable up to 48m (157’) long (model dependent).
- LED message boards connect to the power box with 33m (108’) cables. Additional cables can be used as extensions up to a maximum of 66m (216’) for each message board.
Step 2 – Install the LVS
- Install the LVS so the scan head is:
- in a stable position across the scan area
- perpendicular to the desired vehicle travel direction
- aligned parallel to the ground.
- The transverse beam lens (outer most black lens) should be directly above the desired centre of the track, as illustrated in figure 32.
- Clearance from the bottom of the two lidar scanner lenses to ground should be about 5.3m (17.4’).
- Install the operator console and power box in suitable weather-proof housing.
- Connect the scan head, message board(s), operator console and the printer to the power box via supplied cables.
- Connect single-phase AC mains power to the power box (except for 24 VDC option). If not using a pre-installed power cable, ensure all AC power wires are connected to the correct labelled terminals inside the power box:
| Terminal | Connection |
|---|---|
| L1 | Live (phase) |
| N | Neutral |
| Earth |
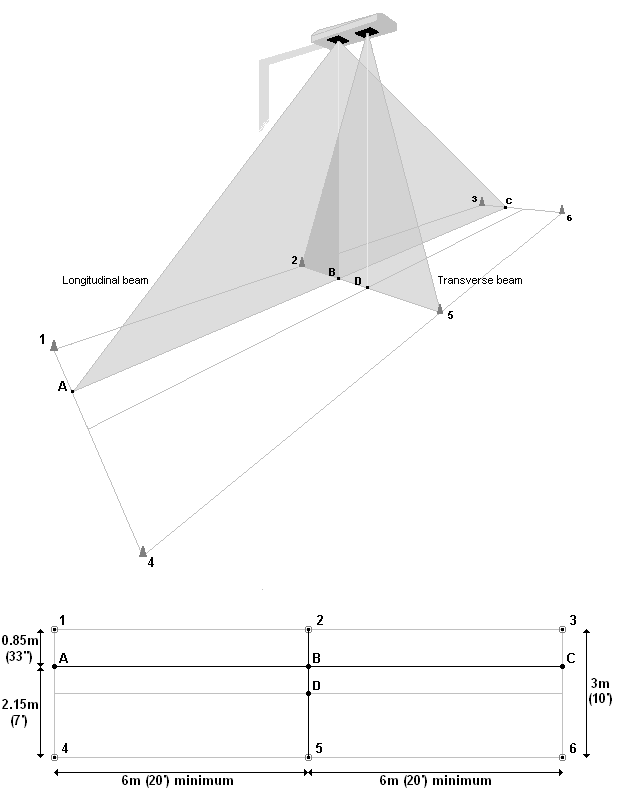
Figure 32 – standard LVS scan area layout for on-road truck and trailer units
Step 3 – Align the scan head
The scan head produces two invisible (infra-red) scanning lidar beams in perpendicular planes as shown in figure 32.
- The longitudinal beam scans along the line between points A and C.
- The transverse beam crosses the longitudinal beam at point B.
- The centre of the track, corresponding to the point directly below the transverse lidar scanner lies at point D.
- Ensure the scan area is clear of vehicles or other objects and power up the system.
- When initialisation is complete, open the SYSTEM screen (figure 33) on the operator console (‘system’ password required).Figure 33 – operator console System screen
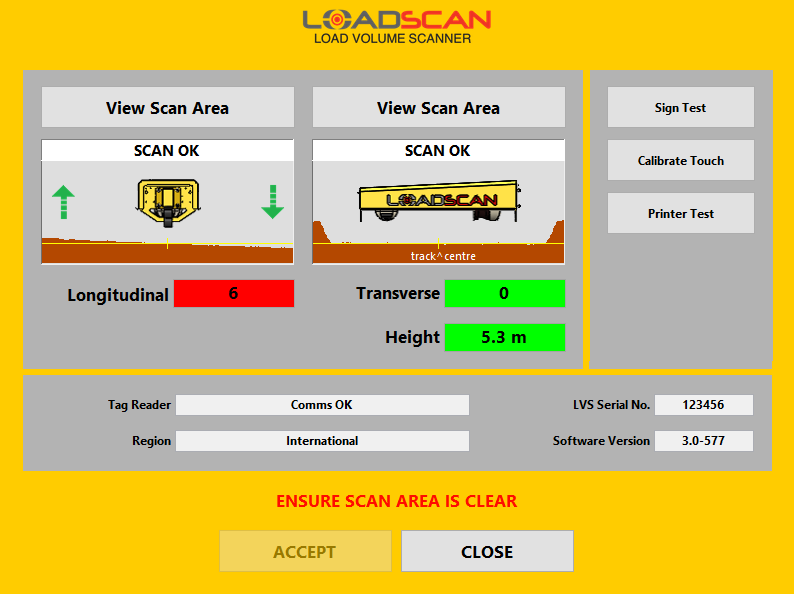
- Profile windows display measured longitudinal and transverse ground profiles. Diagrammatic views of the scan head provide orientation references for these ground profiles.
- The Longitudinal and Transverse indicators show measures of relative alignment between the scan head and the ground in the respective directions.
The Height indicator displays the distance from the scan head to the ground.
f the alignment or height value is acceptable, the background colour of the corresponding indicator is green. If the value is outside the allowable range, the background colour is red. Alignment and height values are also displayed on the message board (with labels ‘T’ for transverse gradient, ‘L’ for longitudinal gradient and ‘H’ for height).
The aim of the following steps is to get all indicators green and both alignment values as close as possible to zero.
- Before making adjustments, check that the status message displayed above both scan profile windows is ‘SCAN OK’.
If either of these displays an error message continuously, discontinue installation and contact Loadscan technical support. - Adjust the angle of the scan head in the longitudinal plane (using the adjustment mechanism on the mounting system), until the longitudinal gradient is as close as possible to zero. Green arrows on the longitudinal ground profile window show the required direction of rotation of the scan head, relative to the scan head diagram in the centre of the profile window.
- Now adjust the angle of the scan head in the transverse plane until the transverse gradient is as close as possible to zero. Green arrows on the transverse ground profile window show the required direction of rotation of the scan head, relative to the scan head diagram in the centre of the profile window.
- Repeat steps 5 and 6 until both the longitudinal and transverse gradients are acceptable (in the range –5 to +5) and as close to zero as practically achievable.
- Check that the HEIGHT indicator is green and, if necessary, adjust the distance between the scan head and the ground, and repeat steps 5-7.
- The ACCEPT button changes from greyed-out to fully visible when the alignment is acceptable. Push this button and enter requested details to record the alignment. If the CANCEL button is pushed the previous alignment profile is retained.
Step 4 – Mark out the scan area
Suitable markers such as traffic cones or barriers must be securely positioned to define a 3m (10’) wide track for the scan area. Trucks must follow this defined pathway during scanning.
The procedure (below) for positioning the scan area delineators describes a method for tracing the position of the transverse and longitudinal lidar beams along the ground.
This requires the use of a handheld survey laser detector capable of detecting infra-red laser beams.
Loadscan supplies a laser detector with every LVS system. Alternative models may be suitable but need to be tested as not all models work with invisible infra-red laser beams.
For mini trucks less than 1.8m (6’) wide
The track centre should be:
- about 0.3m (1’) closer to the longitudinal lidar beam than for standard trucks
- restricted to about 2.4m (8’) wide.
This can be achieved by:
- moving the track outer edge (points 4-6 in figure 32) inwards 600mm (2’) from the standard 3m width position
- leaving the track inner edge at the standard position.
The track outer edge offset from the longitudinal beam is then 1.55m (5’) instead of 2.15m (7’).
For large, off-highway, dump trucks
The track should be widened to the minimum feasible width for the vehicles to be scanned.
Widen the track an equal amount either side of the standard 3m track so that point D in figure 32 remains at the centre of the track.
The height of the scan head may also need to be increased.
Contact your Loadscan representative with your truck specifications for height requirements.
- Open the SYSTEM screen (figure 33) on the operator console (‘system’ password required).
- Use the handheld laser detector to locate the position where the longitudinal scan beam hits the ground at approximately 6m (20’) along the track from the scan head.
- To do this, hold the detector just above ground level with the sensor angled towards the scan head and move slowly across the track until the detector indicates beam detection.
- Find the centre of the beam detection range. Mark the ground at this point. This is point A.
- Use the same method to trace the longitudinal beam back towards the scan head and mark the ground approximately at the point where this line passes directly below the scan head. This is point B.
- Continue to the opposite side of the scan head and once again locate the point where the longitudinal beam hits the ground approximately 6m (20’) from the scan head. Mark the ground at this point. This is point C.
- From point A measure 0.85m (33”) towards the inner side of the scan area (towards the scan head support/base). Mark the ground here. This is point 1.
- Repeat from points B and C to locate and mark points 2 and 3.
- From point A measure 2.15m (7’) towards the further side of the scan area. Mark the ground here. This is point 4.
- Repeat from points B and C to locate and mark points 5 and 6.
- Secure suitable markers/barriers at points 1-6, so that the inside edge of each marker lies on the mark.
- This is the minimum number of demarcation points and additional markers/barriers and a longer restricted track length are suggested.
If the scan head is mounted above an existing roadway or pre-built scan area it may be necessary to adjust the scan head direction and repeat the procedures above until the measured scan area lines up with the desired scan area.
In this Article
The following procedures must be carried out every time an LVS is installed in a new location.
These procedures must be performed to correctly install and align the scan head and define the scan area for vehicles to drive through during scanning.
The exact procedure for physical installation, and the mechanism for scan head alignment adjustments will depend on the scan head mounting design.
The following instructions are not specific to a particular mounting system but all specified dimensions relate to standard installation for on-road truck and trailer units.
For larger off-highway dump trucks, higher mounting and/or wider scan track may be required.
Contact your Loadscan representative for assistance with application-specific installation requirements.
Step 1 – Select a suitable site
- The scan area must be level, or of even gradient not exceeding 5 degrees (9%) and maximum 3-degree (5%) camber.
- The scan area must allow for a 3m (10’) track width, for at least a full truck length before and after the scan head, with a minimum of 6m (20’) of physically restricted width each side.
- Truck and trailer units must:
- have suitable unobstructed access
- be able to approach, pass under and drive clear of the scanner (back of trailer clear of scan head) maintaining a straight line of travel, in either direction throughout.
- A concrete pad is ideal but any hard, non-dusty surface with suitable markers/barriers is adequate.
- The site must be in a dust-controlled environment where only low levels of dust or other visual pollutants in the air are expected.
- 110-240 VAC mains (line) power is required, (except for 24 VDC option).
A suitable power conditioner/surge suppressor should be used to protect the LVS equipment where power quality is poor.
All LVS components should be powered from the same branch circuit.
(Note for Europe: 16A maximum branch circuit breaker, maximum 3m power cord between outlet and power box).A generator with a capacity of at least 1.0 kVA may be used.
Loadscan suggests only inverter-type generators are used and recommends the Honda EU 20i, as it produces good quality power.
- Weather-proof housing is required for the operator console, printer and power box. A site office, portable container/building or sealed kiosk is suitable.
- The operator console can be bench or wall mounted and connects to the power box with a 1.5m (5’) flexible cable. Labelled cable connection ports can be found at the rear of the console.
- The scan head connects to the power box with a flexible cable up to 48m (157’) long (model dependent).
- LED message boards connect to the power box with 33m (108’) cables. Additional cables can be used as extensions up to a maximum of 66m (216’) for each message board.
Step 2 – Install the LVS
- Install the LVS so the scan head is:
- in a stable position across the scan area
- perpendicular to the desired vehicle travel direction
- aligned parallel to the ground.
- The transverse beam lens (outer most black lens) should be directly above the desired centre of the track, as illustrated in figure 32.
- Clearance from the bottom of the two lidar scanner lenses to ground should be about 5.3m (17.4’).
- Install the operator console and power box in suitable weather-proof housing.
- Connect the scan head, message board(s), operator console and the printer to the power box via supplied cables.
- Connect single-phase AC mains power to the power box (except for 24 VDC option). If not using a pre-installed power cable, ensure all AC power wires are connected to the correct labelled terminals inside the power box:
| Terminal | Connection |
|---|---|
| L1 | Live (phase) |
| N | Neutral |
| Earth |

Figure 32 – standard LVS scan area layout for on-road truck and trailer units
Step 3 – Align the scan head
The scan head produces two invisible (infra-red) scanning lidar beams in perpendicular planes as shown in figure 32.
- The longitudinal beam scans along the line between points A and C.
- The transverse beam crosses the longitudinal beam at point B.
- The centre of the track, corresponding to the point directly below the transverse lidar scanner lies at point D.
- Ensure the scan area is clear of vehicles or other objects and power up the system.
- When initialisation is complete, open the SYSTEM screen (figure 33) on the operator console (‘system’ password required).Figure 33 – operator console System screen

- Profile windows display measured longitudinal and transverse ground profiles. Diagrammatic views of the scan head provide orientation references for these ground profiles.
- The Longitudinal and Transverse indicators show measures of relative alignment between the scan head and the ground in the respective directions.
The Height indicator displays the distance from the scan head to the ground.
f the alignment or height value is acceptable, the background colour of the corresponding indicator is green. If the value is outside the allowable range, the background colour is red. Alignment and height values are also displayed on the message board (with labels ‘T’ for transverse gradient, ‘L’ for longitudinal gradient and ‘H’ for height).
The aim of the following steps is to get all indicators green and both alignment values as close as possible to zero.
- Before making adjustments, check that the status message displayed above both scan profile windows is ‘SCAN OK’.
If either of these displays an error message continuously, discontinue installation and contact Loadscan technical support. - Adjust the angle of the scan head in the longitudinal plane (using the adjustment mechanism on the mounting system), until the longitudinal gradient is as close as possible to zero. Green arrows on the longitudinal ground profile window show the required direction of rotation of the scan head, relative to the scan head diagram in the centre of the profile window.
- Now adjust the angle of the scan head in the transverse plane until the transverse gradient is as close as possible to zero. Green arrows on the transverse ground profile window show the required direction of rotation of the scan head, relative to the scan head diagram in the centre of the profile window.
- Repeat steps 5 and 6 until both the longitudinal and transverse gradients are acceptable (in the range –5 to +5) and as close to zero as practically achievable.
- Check that the HEIGHT indicator is green and, if necessary, adjust the distance between the scan head and the ground, and repeat steps 5-7.
- The ACCEPT button changes from greyed-out to fully visible when the alignment is acceptable. Push this button and enter requested details to record the alignment. If the CANCEL button is pushed the previous alignment profile is retained.
Step 4 – Mark out the scan area
Suitable markers such as traffic cones or barriers must be securely positioned to define a 3m (10’) wide track for the scan area. Trucks must follow this defined pathway during scanning.
The procedure (below) for positioning the scan area delineators describes a method for tracing the position of the transverse and longitudinal lidar beams along the ground.
This requires the use of a handheld survey laser detector capable of detecting infra-red laser beams.
Loadscan supplies a laser detector with every LVS system. Alternative models may be suitable but need to be tested as not all models work with invisible infra-red laser beams.
For mini trucks less than 1.8m (6’) wide
The track centre should be:
- about 0.3m (1’) closer to the longitudinal lidar beam than for standard trucks
- restricted to about 2.4m (8’) wide.
This can be achieved by:
- moving the track outer edge (points 4-6 in figure 32) inwards 600mm (2’) from the standard 3m width position
- leaving the track inner edge at the standard position.
The track outer edge offset from the longitudinal beam is then 1.55m (5’) instead of 2.15m (7’).
For large, off-highway, dump trucks
The track should be widened to the minimum feasible width for the vehicles to be scanned.
Widen the track an equal amount either side of the standard 3m track so that point D in figure 32 remains at the centre of the track.
The height of the scan head may also need to be increased.
Contact your Loadscan representative with your truck specifications for height requirements.
- Open the SYSTEM screen (figure 33) on the operator console (‘system’ password required).
- Use the handheld laser detector to locate the position where the longitudinal scan beam hits the ground at approximately 6m (20’) along the track from the scan head.
- To do this, hold the detector just above ground level with the sensor angled towards the scan head and move slowly across the track until the detector indicates beam detection.
- Find the centre of the beam detection range. Mark the ground at this point. This is point A.
- Use the same method to trace the longitudinal beam back towards the scan head and mark the ground approximately at the point where this line passes directly below the scan head. This is point B.
- Continue to the opposite side of the scan head and once again locate the point where the longitudinal beam hits the ground approximately 6m (20’) from the scan head. Mark the ground at this point. This is point C.
- From point A measure 0.85m (33”) towards the inner side of the scan area (towards the scan head support/base). Mark the ground here. This is point 1.
- Repeat from points B and C to locate and mark points 2 and 3.
- From point A measure 2.15m (7’) towards the further side of the scan area. Mark the ground here. This is point 4.
- Repeat from points B and C to locate and mark points 5 and 6.
- Secure suitable markers/barriers at points 1-6, so that the inside edge of each marker lies on the mark.
- This is the minimum number of demarcation points and additional markers/barriers and a longer restricted track length are suggested.
If the scan head is mounted above an existing roadway or pre-built scan area it may be necessary to adjust the scan head direction and repeat the procedures above until the measured scan area lines up with the desired scan area.
